Describe the Events of Mitosis in Sequence
Usually this is due to misalignment of chromosomes along the metaphase plate or a failure of the mitotic spindles to attach to one of the kinetochores. Clinical Relevance Errors of Mitosis.
The 4 Mitosis Phases Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
There are four stages of mitosis.
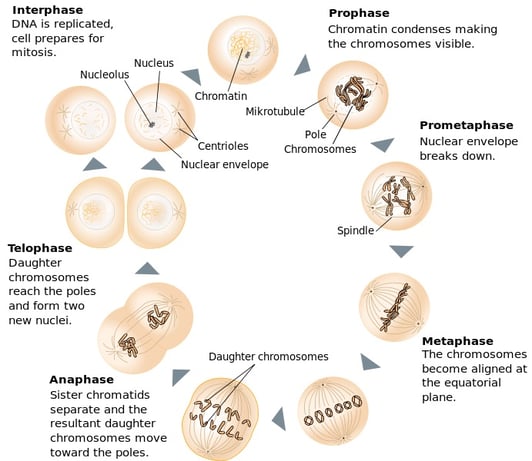
. These are diploid cells with each cell containing a full complement of chromosomes. Prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase1 Prophase. Nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrate.
The mitotic phase is a relatively short period of the cell cycle. Microtubules assemble and their association with centrioles makes the mitotic spindle. This can result in the daughter cells having unequal distribution of chromosomes leaving one cell with one too many and the.
These basic events of mitosis include chromosome condensation formation of the mitotic spindle and attachment of chromosomes to the spindle microtubules. It succeeds the G2 phase and is succeeded by cytoplasmic division after the separation of the nucleus. Some textbooks list five breaking prophase into an early phase called prophase and a late phase called prometaphase.
12 rows 1 Growth of the organism. It alternates with the much longer interphase where the cell. These basic events of mitosis include chromosome condensation formation of the mitotic spindle and attachment of chromosomes to the spindle microtubules.
Mitosis is asexual reproduction. The stages of mitosis are. Mitosis is the phase of the cell cycle where the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei with an equal amount of genetic material in both the daughter nuclei.
There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in a diploid human body cell. An adult human being is made up of billions of cells and all cells have. In prometaphase chromosomes continue to condense kinetochores appear at the centromeres.
After exposure to the antigen only a small number of dendritic cells typically display the antigen on their surface. Mitosis results in 2 diploid cells while meiosis results in 4 haploid cells. These phases occur in this strict sequential order and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase.
In order to accomplish this goal mitosis occurs in four discrete consistently consecutive phases. The spindle apparatus mitotic spindle of microtubules is attached to double-stranded chromosomes. Discuss the following problem.
1 prophase 2 metaphase 3 anaphase and 4 telophase. Name the stages of mitosis in order and describe the behavior and structure of the chromosomes at each stage. At the end of cytokinesis two genetically identical daughter cells are produced.
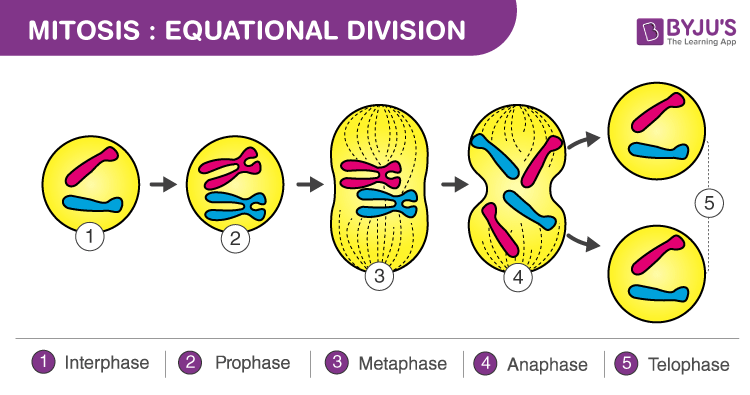
Prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. I G1 phase ii S phase iii G2 phase G1 phase It is the stage during which the cell grows and prepares its DNA for replication. Only two pairs of chromosomes are shown in the diagrams below.
Prophase is the first stage of mitosis. Mitosis is the process in which a cell splits itself into 2 identical daughter cells. Describe the four stages of mitosis.
The spindle fibres contract and separate the sister chromatids from each other. Cytokinesis The process during cell division in which the cytoplasm divides is. Interphase is divided into three phases.
The nuclear membrane then reforms and the chromosomes begin to decondense into their interphase conformations. The correct order sequence of events during mitotic division in living organisms include the following. Although many of the details of mitosis vary among different organisms the fundamental processes that ensure the faithful segregation of sister chromatids are conserved in all eukaryotes.
Define mitosis and list its four stages. Mitosis is important because it ensures that all new cells that are generated in a given organism will have the same number of chromosomes and genetic information. Mitosis is a division of the nucleus plus cytokinesis and produces two identical daughter cells during prophase P metaphase M anaphase A and telophase T.
What are the stages of metaphase. Prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. Synapsis occurs during meiosis prophase I but not in mitosis.
In this phase the cell is metabolically active. Sister chromatids then separate from each other and move to opposite poles of the spindle followed by the formation of daughter nuclei. Mitosis is essential for the growth of the cells and the replacement of worn-out cells.
In prophase chromosomes condense and become visible spindle fibers emerge from the centrosomes nuclear envelope breaks down nucleolus disappears Prometaphase is the second stage of mitosis. Chromatin into chromosomes the nuclear envelope break down chromosomes attach to spindle fibres by their centromeres 2 Metaphase. Association of microtubules with sister chromatids takes place in prophase.
While Meiosis is sexual reproduction that results in gametes. Chromatin fibers condense to form chromosomes. It is the period during which the cell experiences growth and DNA replication in an orderly manner.
Prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. The sister chromatids are pulled to opposite ends of the cell - the cell. Mitosis ends with telophase or the stage at which the chromosomes reach the poles.
Errors in mitosis usually occur during metaphase. There is a very easy way to remember the stages of mitosis. Explain the significance of mitosis and describe the process.
It begins prior to the end of mitosis in anaphase and completes shortly after telophasemitosis. The disintegration of the nuclear membrane. Cells produced through mitosis are different from those produced through meiosis.
Mitosis consists of four basic phases. Before exposure to a foreign antigen T cells with receptors specific for the antigen are a tiny fraction of the T cells-on the order of 1 in 105 or 1 in 106 T cells. Mitosis consists of four basic phases.
Centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell. There is only one division in mitosis while in meiosis there are 2 divisions. List the stages of mitosis and briefly describe the events that occur in each.
Chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate centre of the cell 3 Anaphase.

Can You Brief The Sequence Of Events Occurring During Mitosis Neet


No comments for "Describe the Events of Mitosis in Sequence"
Post a Comment